Understanding Testicular Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Testicular cancer is a relatively rare form of cancer that develops in the testicles, the male reproductive glands located within the scrotum. While testicular cancer accounts for a small percentage of all cancer diagnoses, it is the most common cancer in young men aged 15 to 35. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for testicular cancer, aiming to raise awareness and provide valuable information for early detection and management.
Symptoms of Testicular Cancer:
- Lump or Swelling: The most common symptom of testicular cancer is a painless lump or swelling in one or both testicles. The lump may feel firm or hard and may vary in size.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some men may experience pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum, although this is less common.
- Changes in Testicular Size or Shape: Testicular cancer may cause changes in the size or shape of the testicles, often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the scrotum.
- Lower Back Pain: In advanced cases, testicular cancer may spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs, leading to symptoms such as lower back pain, shortness of breath, or swelling in the legs.
Causes of Testicular Cancer:
- The exact cause of testicular cancer is not fully understood, but certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These risk factors include:
- Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle)
- Family history of testicular cancer
- Previous history of testicular cancer
- Genetic conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome
- Prenatal exposure to certain environmental factors or medications
Diagnosis of Testicular Cancer:
- Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, including a careful examination of the testicles and scrotum, to check for lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities.
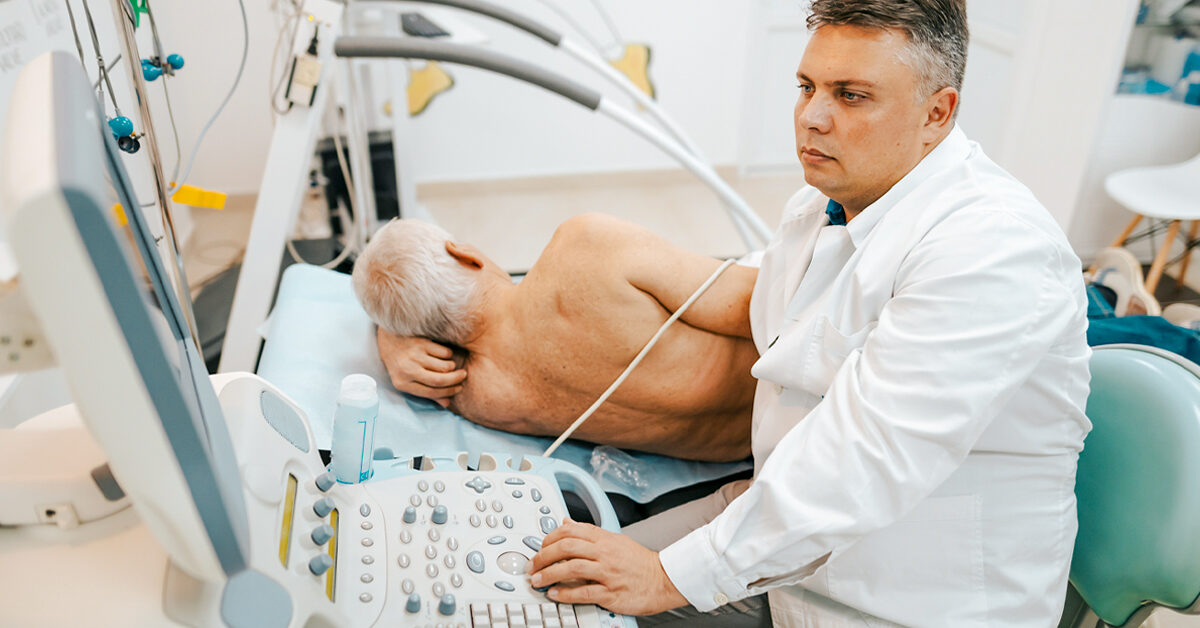
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound imaging of the scrotum is often used to evaluate testicular lumps or abnormalities. Ultrasound can help determine whether a lump is solid (potentially cancerous) or fluid-filled (such as a cyst).
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be performed to measure levels of tumor markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which may be elevated in cases of testicular cancer.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample from the testicle for further analysis. However, biopsies are not routinely performed for suspected testicular cancer due to the risk of spreading cancer cells.
Treatment Options for Testicular Cancer:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for testicular cancer is surgical removal of the affected testicle, a procedure known as radical inguinal orchiectomy. In cases where the cancer has spread, additional surgeries may be necessary to remove lymph nodes or other affected tissues.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be recommended for certain types and stages of testicular cancer to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence. Chemotherapy drugs may be administered before or after surgery, depending on the specific situation.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used to target and destroy cancer cells in the testicle or nearby lymph nodes. It is often used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy for advanced or aggressive cancers.
Conclusion:
Testicular cancer is a relatively rare but highly treatable form of cancer that primarily affects young and middle-aged men. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential for successful outcomes. If you notice any unusual changes in your testicles or experience symptoms such as a painless lump, swelling, or discomfort, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management.
To book online select the date and time that suits you best – alternatively, please contact us with any questions via the chat, call or email links provided.
Telephone: 020 7101 3377

