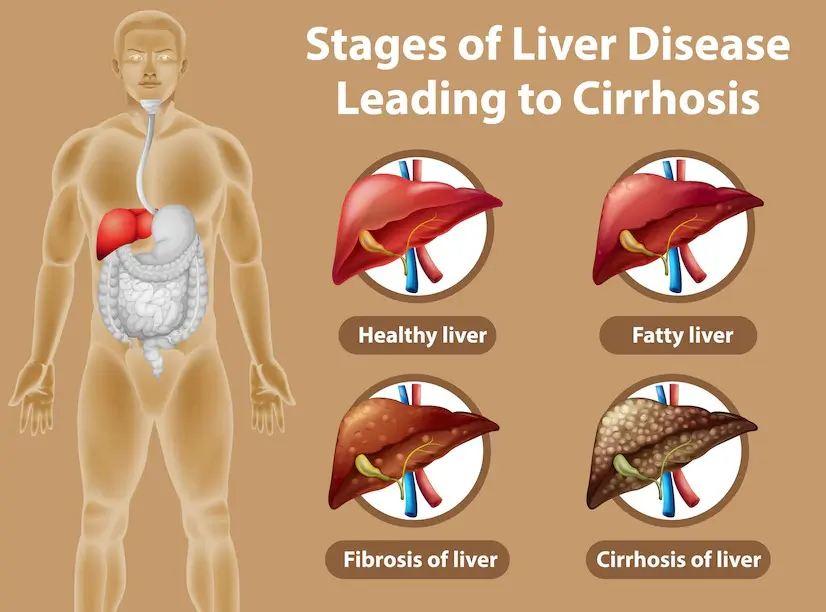
Liver health, often referred to as hepatic well-being, encompasses a range of liver impairments that disrupt its natural functions. Factors like viruses, infectious agents, medications, toxins, autoimmune disorders, and genetic disposition contribute to liver damage. The consequences vary, spanning from compromised liver function and inflammation (hepatitis) to the formation of scar tissue within the liver (cirrhosis), total loss of liver function (liver failure), and, in severe cases, liver cancer. These damages can also lead to changes in the liver’s size and structure, detectable through imaging methods such as ultrasound.
The prominence of ultrasound in diagnosing and monitoring hepatic diseases has significantly grown. Its proficiency lies in generating detailed images capable of promptly identifying irregularities. Ultrasound offers a non-invasive approach, evaluating changes in size, shape, and texture, serving as indicators for specific hepatic conditions. Its applications range from detecting viral infections and fatty infiltration to cirrhosis, alongside tracking the evolution of changes over time. Furthermore, ultrasound proves valuable in evaluating bleeding disorders, assisting in transplantation surgery planning, and guiding biopsy procedures.
Ultrasound serves as a non-invasive imaging technique widely adopted for diagnosing and monitoring liver conditions like cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, and cysts. By utilizing sound waves, it constructs intricate images of the liver’s internal structures, elevating diagnostic accuracy. This discourse delves into the journey of diagnosing liver disease through ultrasound.
Ultrasound stands as a diagnostic tool for assessing liver dimensions, and structure Through sound wave emission, translated into images on a computer screen, medical experts engage in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing various liver-related conditions.
Liver evaluation via ultrasound considers multiple parameters—size, contour, surface characteristics, echogenicity, and the presence of masses or infection. Doppler ultrasound further examines blood flow within the liver and surrounding vessels.
Anomalies detected during ultrasonography may prompt additional exploration, involving advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI for deeper insights. Preceding biopsies, ultrasound guides fine needle aspiration for tissue analysis. By harmonizing ultrasound with other imaging modalities, holistic images support precise diagnoses and informed treatment strategies for suspected liver-related conditions.
Ultrasound emerges as a dependable, non-intrusive method for tracking chronic liver conditions like cirrhosis. Its cost-effectiveness and accessibility make it suitable for both early detection and ongoing monitoring of liver ailments.
This segment delves into employing ultrasound for liver disease monitoring.
Sequential ultrasound exams are pivotal for meticulous liver tracking. Effective follow-ups empower physicians to evaluate treatment efficacy and make adjustments. The application of standard ultrasounds for diagnostic imaging has yielded promising results in the progressive monitoring of liver disease.
Standard ultrasounds provide precise images, serving as benchmarks for future assessments. Follow-up scans pinpoint specific changes since the initial scan, helping doctors assess treatment impacts. In progressive liver diseases, follow-ups reveal the influence of lifestyle changes or therapies on liver health.
While more complex tests like Elastography (Fibro scan), Advanced Liver Ultrasound, Contrast Enhanced Sonography, Radionuclide Scanning, MRI, and CT scans can provide detailed insights into underlying conditions affecting liver function, they often complement the comprehensive information already gleaned from standard ultrasounds. The latter excels in delivering accurate, routine imaging assessments over time.
Ultrasound proves a versatile tool, overseeing liver diagnostics encompassing anatomy visualization, blood flow examination, and disease progression tracking. It identifies indicators of inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and assesses cystic lesions. Ultrasound effectiveness in diagnosing liver complications is well-received by patients due to its non-radiation nature. In this procedure, sound waves are transmitted into the body, forming clear images on a screen, unveiling insights into size, shape, and internal components.
Significantly, ultrasound showcases cost-effectiveness in chronic liver disease monitoring. It often eliminates or minimizes the requirement for supplementary tests like radiography or biopsies, prominent in other imaging methods.
In summary, ultrasound stands as an invaluable asset in diagnosing and overseeing liver diseases. Its non-intrusive nature and precision render it a reliable substitute for conventional liver diagnostics and monitoring, offering patients a less invasive assessment option.

