Understanding Liver Cirrhosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
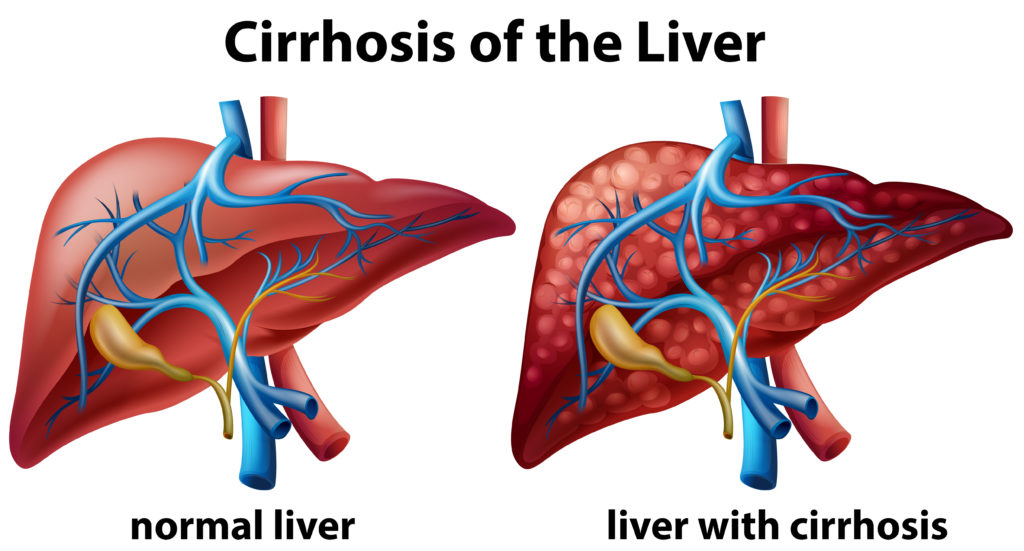
Liver cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. Each time your liver is injured, it tries to repair itself. In the process, scar tissue forms. As cirrhosis progresses, more and more scar tissue forms, making it difficult for the liver to function.
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis
Common Causes
-
Chronic Alcohol Abuse
- Mechanism: Excessive alcohol consumption over a long period can lead to liver damage and cirrhosis.
- Prevention: Limiting alcohol intake and seeking help for alcohol dependence.
-
Chronic Viral Hepatitis
- Hepatitis B and C: Both types can cause long-term liver inflammation and damage.
- Prevention: Vaccination for hepatitis B and safe practices to prevent hepatitis C infection, such as avoiding sharing needles and practicing safe sex.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- Mechanism: Accumulation of fat in the liver not related to alcohol intake can lead to inflammation and scarring.
- Risk Factors: Obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol.
- Prevention: Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle.
-
Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Mechanism: The immune system attacks liver cells, causing inflammation and damage.
- Prevention: Currently, there is no known prevention, but early diagnosis and treatment can manage the condition.
-
Bile Duct Diseases
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): These conditions damage the bile ducts, leading to cirrhosis.
- Prevention: There are no specific preventive measures, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the diseases.
-
Genetic Diseases
- Hemochromatosis: Excess iron buildup in the liver.
- Wilson’s Disease: Excess copper buildup in the liver.
- Prevention: Genetic counseling and regular monitoring for those with a family history.
Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis
Early Symptoms
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness.
- Weakness: General feeling of weakness.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased desire to eat.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss.
Advanced Symptoms
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to high bilirubin levels.
- Edema: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid retention.
- Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
- Itching: Persistent itching due to bile products in the skin.
- Spider Angiomas: Small, spider-like blood vessels visible under the skin.
- Bruising and Bleeding: Increased tendency to bruise or bleed due to decreased production of clotting proteins.
- Confusion and Memory Loss: Hepatic encephalopathy caused by the buildup of toxins in the brain.
Diagnosis of Liver Cirrhosis
Medical History and Physical Exam
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s history of liver disease, alcohol use, medications, and other risk factors.
- Physical Examination: Checking for physical signs of liver disease, such as jaundice, swelling, and spider angiomas.
Blood Tests
- Liver Function Tests: Measuring levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins to assess liver function.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checking for anemia and clotting problems.
- Viral Hepatitis Tests: Detecting hepatitis B and C infections.
Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: Initial imaging test to check for liver abnormalities.
- CT Scan and MRI: Detailed imaging to assess liver size, structure, and blood flow.
- Transient Elastography: A specialized ultrasound to measure liver stiffness (fibrosis).
Liver Biopsy
- Procedure: Removing a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination.
- Purpose: Confirming the diagnosis and assessing the extent of liver damage.
Management of Liver Cirrhosis
Lifestyle Changes
- Avoiding Alcohol: Complete abstinence from alcohol to prevent further liver damage.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limiting salt intake to reduce fluid retention.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of complications.
Medications
- Antiviral Drugs: Treating chronic hepatitis B and C infections to reduce liver damage.
- Diuretics: Reducing fluid buildup in the body.
- Beta-Blockers: Lowering blood pressure in the portal vein to reduce the risk of bleeding from varices.
- Lactulose and Rifaximin: Treating hepatic encephalopathy by reducing toxin levels in the blood.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Addressing nutritional deficiencies.
Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
- Regular Blood Tests: Monitoring liver function, electrolytes, and clotting status.
- Imaging Tests: Periodically assessing liver structure and detecting complications such as liver cancer.
- Endoscopy: Screening for varices and other gastrointestinal complications.
Advanced Treatments
- Liver Transplant: For patients with end-stage liver disease or liver cancer who meet the criteria for transplantation.
- Surgical Procedures: Treating complications such as variceal bleeding or ascites.
Managing Complications
- Ascites: Reducing fluid accumulation through diet, medications, or paracentesis (removal of fluid from the abdomen).
- Variceal Bleeding: Preventing and treating bleeding with medications, endoscopic procedures, or surgery.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Managing cognitive symptoms with medications and dietary changes.
Conclusion
Liver cirrhosis is a serious condition that requires comprehensive management to prevent progression and manage complications. Early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, medication, regular monitoring, and advanced treatments can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with cirrhosis. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options empowers patients and healthcare providers to work together in managing this chronic liver disease effectively.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, please contact London Private Ultrasound. Visit our website at www.londonsono.com, call us at 02071013377, or email us at [email protected]. Take proactive steps towards maintaining your liver health today.

