Puberty is a pivotal stage in human development when a child’s body begins to transition into an adult body capable of reproduction. This period is marked by a series of physical and hormonal changes triggered by the brain’s signals to the gonads (the ovaries in girls and the testes in boys), leading to the production of sex hormones. These hormones are responsible for the characteristic changes of puberty, including growth spurts, development of secondary sexual characteristics, and changes in mood and behavior.
Stages of Puberty in Girls
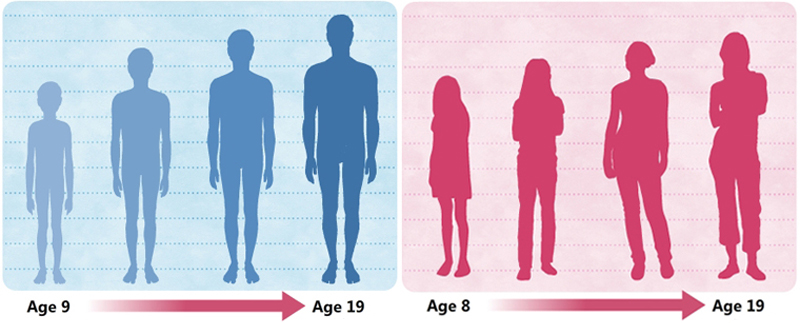
For girls, puberty typically begins between the ages of 8 and 13 and can last from 2 to 5 years. Key stages include:
- Breast development: Often the first sign, starting with small, firm breast buds.
- Pubic and underarm hair growth: Hair becomes coarser and darker.
- Growth spurt: Rapid height increase, usually peaking about 2 years after the onset of puberty.
- Menstruation (menarche): Usually begins 2 to 3 years after breast development starts, indicating the ability for reproduction, though regular cycles may take several years to establish.
Stages of Puberty in Boys
Boys typically enter puberty slightly later than girls, around the ages of 9 to 14, and changes can continue into their early twenties. Key developments include:
- Testicular enlargement: The first noticeable sign, followed by changes in the texture and appearance of the scrotum.
- Penile growth: Occurs approximately a year after the testicles begin enlarging.
- Pubic, underarm, facial, and body hair growth: Hair becomes thicker and darker.
- Voice deepening: As the larynx enlarges, the voice may “crack” before settling into a deeper tone.
- Growth spurt: Typically occurs later than in girls, with most rapid growth occurring late in puberty.
Hormonal Changes and Their Effects
Puberty is driven by an increase in sex hormones – estrogen in girls and testosterone in boys. These hormones not only contribute to the physical changes but also affect mood and emotional state. It’s common for adolescents to experience mood swings, increased sensitivity, and changes in interest and self-identity during this time.
The Importance of Understanding Puberty
Understanding the stages and effects of puberty is crucial for several reasons:
- Health education: Knowledge about puberty can help young people understand and cope with the changes they are experiencing.
- Parental support: Parents who understand the phases of puberty can better support their children through these transitions.
- Early or delayed puberty: Recognizing the signs of early or delayed puberty is important for identifying potential health issues. Early (precocious) puberty or delayed puberty can signal underlying medical conditions requiring evaluation and possibly treatment.
1- Pelvic Ultrasound for Girls during the Puberty
A pelvic ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to examine the organs and structures within the pelvis. For girls during puberty, this procedure can provide valuable information regarding the development and health of their reproductive organs. Here’s an overview:
Purpose of a Pelvic Ultrasound During Puberty
- Assessment of Reproductive Organs: It helps in evaluating the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic structures for any abnormalities.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Can assist in diagnosing causes of irregular periods, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), ovarian cysts, or other hormonal imbalances.
- Developmental Anomalies: Helps identify congenital abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
- Pelvic Pain: Aids in finding the cause of pelvic pain, which could be due to various conditions like ovarian cysts or other gynecological issues.
- Monitoring Growth: Tracks the development and growth of reproductive organs during puberty.
Procedure
- Preparation: The patient may be asked to drink water before the exam to ensure a full bladder, which provides a better view of the pelvic organs.
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: A gel is applied to the lower abdomen, and a transducer is moved over the area to capture images.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: In some cases, a transvaginal ultrasound might be recommended for a closer look at the pelvic organs. However, this is typically more common in adult women and may not be necessary or comfortable for girls during puberty.
What to Expect
- Non-invasive and Painless: The procedure is generally painless, though slight discomfort may be felt from the pressure of the transducer.
- Duration: It usually takes about 20-30 minutes.
- Safety: Pelvic ultrasounds are safe and do not involve radiation.
Results
The results of a pelvic ultrasound can provide critical information for diagnosing and managing various conditions. The images are analyzed by a radiologist, who will provide a report to the referring physician. Based on the findings, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
2- Testicular Ultrasound for Boys during the Puberty
A testicular ultrasound, also known as a scrotal ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging test used to examine the testicles and surrounding structures in the scrotum. For boys during puberty, this procedure can provide valuable information regarding the development and health of their reproductive organs. Here’s an overview:
Purpose of a Testicular Ultrasound During Puberty
- Assessment of Testicular Development: Helps evaluate the size, shape, and development of the testicles.
- Detection of Abnormalities: Can identify masses, cysts, or other abnormalities in the testicles.
- Evaluation of Pain or Swelling: Assists in diagnosing causes of testicular pain or swelling, such as testicular torsion, epididymitis, or hydrocele.
- Fertility Concerns: Provides information on conditions that could affect future fertility.
- Trauma: Assesses damage from injury to the testicles.
Procedure
- Preparation: Typically, no special preparation is needed.
- Positioning: The patient lies on their back with the scrotum supported by a towel.
- Transducer Application: A gel is applied to the scrotum to facilitate the movement of the transducer, which emits sound waves to create images of the testicles and surrounding structures.
What to Expect
- Non-invasive and Painless: The procedure is generally painless, though some slight discomfort may be experienced from the pressure of the transducer.
- Duration: The ultrasound usually takes about 15-30 minutes.
- Safety: Testicular ultrasounds are safe and do not involve radiation.
Results
The results of a testicular ultrasound can provide critical information for diagnosing and managing various conditions. The images are analyzed by a radiologist, who will provide a report to the referring physician. Based on the findings, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
Common Conditions Identified
- Testicular Torsion: A medical emergency where the testicle twists, cutting off its blood supply.
- Epididymitis: Inflammation of the epididymis, often due to infection.
- Hydrocele: A fluid-filled sac around a testicle, causing swelling.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins within the scrotum, which can affect fertility.
- Tumors: Identification of benign or malignant masses.
3- Breast Ultrasound during the Puberty
A breast ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the internal structures of the breast. For girls during puberty, this procedure can be particularly useful for evaluating breast development and identifying any abnormalities. Here’s an overview:
Purpose of a Breast Ultrasound During Puberty
- Assessment of Breast Development: Helps evaluate the normal growth and development of breast tissue.
- Detection of Lumps or Masses: Can identify cysts, benign tumors, or other abnormalities in the breast tissue.
- Evaluation of Pain or Swelling: Assists in diagnosing causes of breast pain, tenderness, or swelling.
- Monitoring Fibrocystic Changes: Helps differentiate between normal fibrocystic changes and more serious conditions.
- Guidance for Biopsies: Used to guide needle biopsies for sampling suspicious areas.
Procedure
- Preparation: Typically, no special preparation is needed.
- Positioning: The patient lies on her back with her arm raised above her head to allow for better access to the breast tissue.
- Transducer Application: A gel is applied to the breast, and a transducer is moved over the area to capture images.
What to Expect
- Non-invasive and Painless: The procedure is generally painless, though slight discomfort may be felt from the pressure of the transducer.
- Duration: It usually takes about 15-30 minutes.
- Safety: Breast ultrasounds are safe and do not involve radiation.
Results
The results of a breast ultrasound can provide critical information for diagnosing and managing various conditions. The images are analyzed by a radiologist, who will provide a report to the referring physician. Based on the findings, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
Common Conditions Identified
- Fibroadenomas: Non-cancerous lumps common in teenage girls and young women.
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can be painful but are usually benign.
- Infections or Abscesses: Infections in the breast tissue that may require treatment.
- Gynecomastia: In boys, ultrasound can help assess breast tissue development and identify any abnormal growth.
How Healthcare Providers Can Help
Healthcare professionals play a key role in guiding families through puberty. This support can include:
- Providing information and reassurance about normal developmental changes.
- Assessing for and managing any deviations from typical puberty progression, such as precocious puberty or delayed puberty.
- Addressing any concerns related to physical or emotional health during adolescence.
Puberty is a natural, albeit complex, part of growing up, with variations in timing and progression among individuals. Open conversations between young people, their families, and healthcare providers about puberty can promote healthy development and ease the transition into adulthood.
To book online select the date and time that suits you best – alternatively, please contact us with any questions via the chat, call or email links provided.
Telephone: 020 7101 3377

